
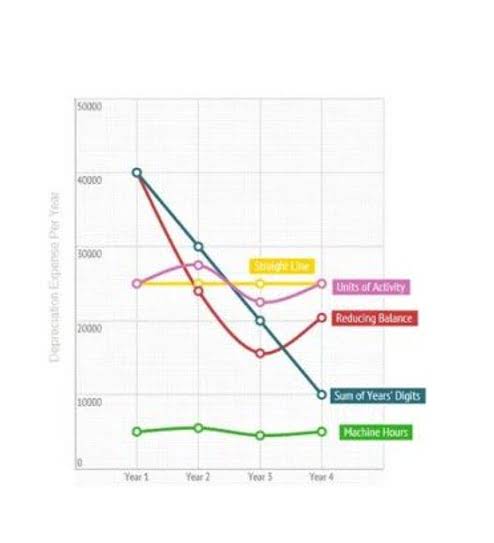
Operating income, on the other hand, focuses solely on profits generated from core business operations, excluding non-operating factors. Some assets give up their services gradually rather than all at once. To estimate depreciation, the accountant must predict both how long the asset will continue to provide useful services and how much of its potential to provide these services will be used up in each period.
Accounting implications of tariffs
- Which involves at credit to inventory, decreasing your assets and a debit to the cost of goods, sold account, increasing your expenses.
- We also made a distinction between product costs and period costs.
- Whenever costs are estimated in advance, there will be some discrepancy between the prediction and the reality.
- This service / information is strictly confidential and is being furnished to you solely for your information.
Bajaj Financial Securities Limited (“Bajaj Broking” or “Research Entity”) is regulated by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (“SEBI”) and is licensed to carry on the business of broking, depository services and related activities. Investors typically compare a company’s operating margin to that of its industry peers to assess relative performance. This means the company retains 20% of its revenue as operating profit. Includes interest, taxes, and one-time items like extraordinary gains/losses. To assess how efficiently a company generates profit from its core operations.
Good News! We have found the answer to this question!
For example, if a company uses the accrual method to recognize revenue, it will recognize revenue from a sale even if the cash has not yet been received. Under the accrual method, revenue is recognized when it is earned, regardless of when cash is net income recognition always increases: received. This method is used by most businesses because it provides a more accurate picture of the company’s financial performance. In the US, where accounting standards are called the “generally accepted accounting principles,” or GAAP, the standard with the same name is referred to as Topic 606. There are some technical differences between IFRS 15 and Topic 606, but they aren’t big enough to worry about here. They both deal with the core issue of accrual accounting, which is when to recognize revenue and expenses so that the net income for a fiscal period is a more useful indicator of the financial performance of a company.
Solved Net income recognition always increases:Multiple

If you build something better than it needs to be built for the price being charged to the customer, you’re wasting your own money. Companies try to build products to a certain level of reliability, and then charge more for higher quality and less for lower quality. They know from their engineering, what the breakage rate will be on average. If any part of that isn’t clear, then the revenue recognition situation isn’t clear. The last step in recognizing revenue is usually straightforward. You deliver the goods or you deliver the service, and at that point you have a legal right to be paid.

- That means recognizing $40,000 of expense with a debit to the depreciation expense account.
- The basic issue for revenue and expense recognition is what to do when the process of producing a good or service, delivering it to the customer, and getting paid by the customer, spans a fiscal year-end.
- In this case, however, it’s a credit, so that’s disclosed as a kind of revenue called “gain on disposal of assets.”
- If cash is paid after an expense is recognized, you create a liability.
- As noted in the response to Question 2-1, price changes due to tariffs would be evaluated as variable consideration or a contract modification.
- The Stock Exchange, Mumbai is not answerable, responsible or liable for any information on this Website or for any services rendered by our employees, our servants, and us.
In conclusion, both Operating Income and Net Income are essential metrics for evaluating a company’s financial performance, but they provide different perspectives. Operating income focuses on a company’s ability to generate profit fixed assets from its core business, while net income gives a comprehensive view after accounting for all revenues, expenses, and taxes. For beginners, understanding both metrics helps in making more informed decisions about a company’s profitability and operational efficiency. They are when a company estimates a future costs that is likely to face, such as losing a lawsuit or having to clean up a mining site.
But there are lots of other costs in running a business that are not directly related to specific sales events, like the salary of the CEO or the interest on a bank loan. Those are called period costs as opposed to product costs, and I’ll discuss those later in this lesson. While some contracts may have price adjustment clauses that automatically allow for an increase in price for an increase in tariffs, many will not.
- Companies may face complex operational and compliance challenges due to the number of items potentially subject to US imposed tariffs, possible reciprocal tariffs, and ongoing uncertainty surrounding tariff policies.
- Bad debts are when you sell to someone on credit and they fail to pay the invoice.
- Getting more for the truck now does not change how much it cost us when we bought it or how much we’ve depreciated it since.
- If the customer walks out the door with a litre of milk after paying for it, they own it.
- To recognize revenue, you have to examine and parse the contract with the customer.
- When something besides cash is offered by the customer, that has to be assigned a value, too, and considered part of the transaction price.
The LIFO cost of the ending inventory is the cost of the oldest units in the cost of goods available. In the first case, we have a $40,000 depreciation expense at the end of year one, and another $40,000 depreciation expense at the end of year two, plus a loss of $20,000 when we sold it. So here we can see that the impact on the income statement over the life of the truck is equal to the original purchase price, less the resell price that we got for it. Here we’re paying $200,000 cash for it, so that’s just moving value from one asset class to another. The only account shown here that affects the income statement is the credit to revenue. Paying six months of rent in advance means a monthly rent expense of 1/6th of the amount you paid.

In addition, the newly imposed tariffs could create other pre-tax impacts that companies will need to assess for related tax accounting consequences. For example, the impairment of long-lived assets and goodwill may have an impact on a company’s deferred taxes. When there is no market available to the company, it may have to determine the characteristics of a market participant to which it would hypothetically sell the asset if it were seeking to do so. Once the market participant characteristics are determined, the company would identify the assumptions that those market participants would consider when pricing the asset. The company should construct a hypothetical or “most likely” market for the asset based on its own assumptions about what market participants would consider in negotiating a sale of the asset or transfer of the liability. Net income includes all revenues and expenses, including operating and non-operating items such as taxes, interest, and one-time events.
Expense Recognition
Think about performance obligations and about the transaction price. If you’re studying this course along with someone else, discussing the ins and outs of IFRS 15 with them can be a great help. The example of the dishwasher and the warranty service that I gave before is an example of separate benefits. However, if Accounting for Marketing Agencies you’re a car dealership and the customer expects not only a new car, but one with that “new car smell.” The new car smell is not distinct from the car itself.

Skriv et svar